
SANKEN
The University of Osaka
大阪大学
産業科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2017/07/28
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name趙成訓 CHO Sunghun
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Affiliation大阪大学 産業科学研究所
先端ハード材料研究分野
SANKEN, The University of Osaka
Department of Advanced Hard Materials -
研究キーワード
Research Keywordsナノセラミック材料
光触媒
チタネート構造
メカニズム分析
水分解
DSSCs
Nano ceramic materials
Photocatalyst
Titanate structure
Mechanism analysis
Water splitting
DSSCs
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
チタネートのナノ構造の制作及び特性分析
Titanate nanostructures analysis and characterizations
研究の背景 Background of the Research
チタネートナノ構造体は高いイオン交換効率及びロード、チューブ、リボンなどの多様な形態を利用して様々な所に応用できる。本研究者はこのような点に注目し、チタネートの形成メカニズムを分析しこれを利用して光触媒ナノ材料の作成及び環境にやさしい材料の応用を把握し、水分解水素生産材料及びDSSCの応用研究を進めている。
Titanate nanostructures can be potential materials in the various fields of application due to their inherent ion-exchange capabilities and unique morphologies. I focus on the parameters on formation of Titanate nanostructure materials for the photo-catalyst nano-materials for environmental cleaning, water splitting system(hydrogen generation), and Dye Sensitized Solar Cell (DSSC).
研究の目標 Research Objective
本研究は“水熱合成法を利用して作製したチタネートのナノ構造分析及び特徴”を介してそれぞれのチタネートナノ構造形成を把握し、それぞれの形態が形成される条件をマイクロ波水熱合成法及びアルカリ水溶液法を用いて実施する。またこれを利用して新たな光触媒材料を発展させ、その特徴を発展させる。
The main objective of the research is “Titanate nanostructures analysis and characterizations using hydrothermal process” is aimed to investigate synthesis parameters on the formation of titanate nanostructures from titanium dioxide powders through the Microwave assisted hydrothermal and Aqueous solution with alkali process. Apply this knowledge for development of new photocatalyst materials with improved performance.
研究図Figures
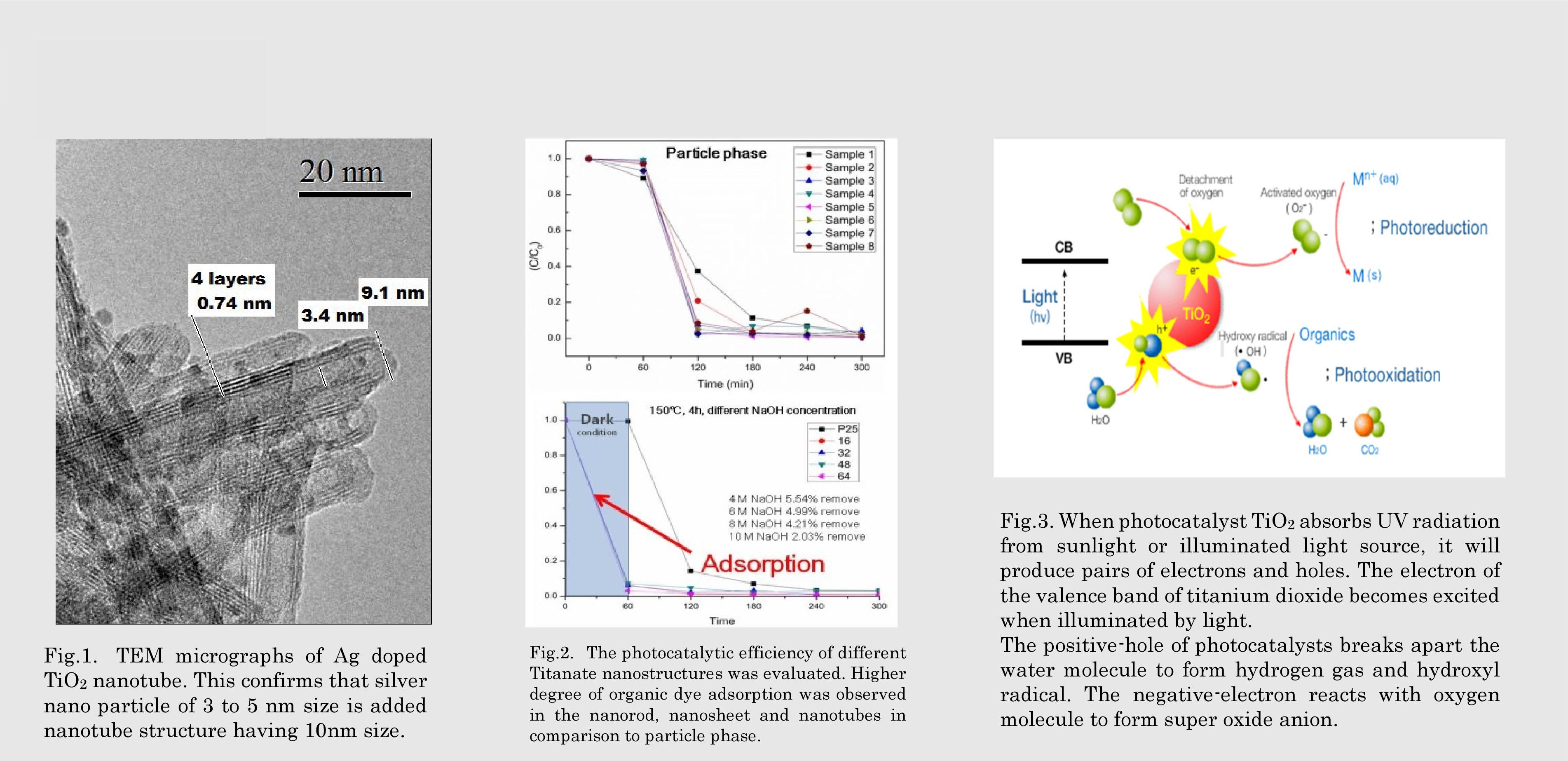
Fig.3. When photocatalyst TiO2 absorbs UV radiation from sunlight or illuminated light source, it will produce pairs of electrons and holes. The electron of the valence band of titanium dioxide becomes excited when illuminated by light. The positive-hole of photocatalysts breaks apart the water molecule to form hydrogen gas and hydroxyl radical. The negative-electron reacts with oxygen molecule to form super oxide anion.
論文発表 / Publications
Catalysis Today., 266, 46 (2016). Materials Chemistry and Physics., 145, 297 (2014).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- shcho
 sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp
sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp - http://www.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/organization/sec/sec_03/