IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/05/05
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name篠田弘造 Kozo SHINODA
准教授 Associate Professor -
所属
Professional Affiliation東北大学多元物質科学研究所
計測研究部門 放射光可視化情報計測研究分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Division of Measurements, Synchrotron Radiation Microscopy and Informatics -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords機能性粒子素材
環境保全
X線利用局所構造解析
particulate functional materials
environmental preservation
local structure analysis using x-ray
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
水環境からの環境負荷化学種除去のための多孔質吸着材粒子開発
Development of porous adsorbing materials to remove toxic elements from water
研究の背景 Background
実用的な素材開発のためには、個々の特性のみでなく利用されるシステム全体を考慮する必要があります。たとえば、粒子状吸着材による水環境からの有害化学種除去では、吸着特性向上だけでなく、脱着プロセスの単純化と高効率化を可能にするような特性最適化が必要です。また、物性と密接に関係する局所構造を知ることが開発推進にとって重要です。
For development of functional materials suitable for practical use, considering not only each physicochemical property but also the whole system using the materials is necessary. For example, for the particulate absorbent using to remove toxic chemical species from the water environment, the material requiring a large amount of treatment agents in desorption process is not suitable for use, even if it has high adsorption properties. Therefore, simplification and efficiency of the desorbing process is desired in order to establish the practical water treatment system. The clarification of relation between the properties and local structure is very important.
研究の目標 Outcome
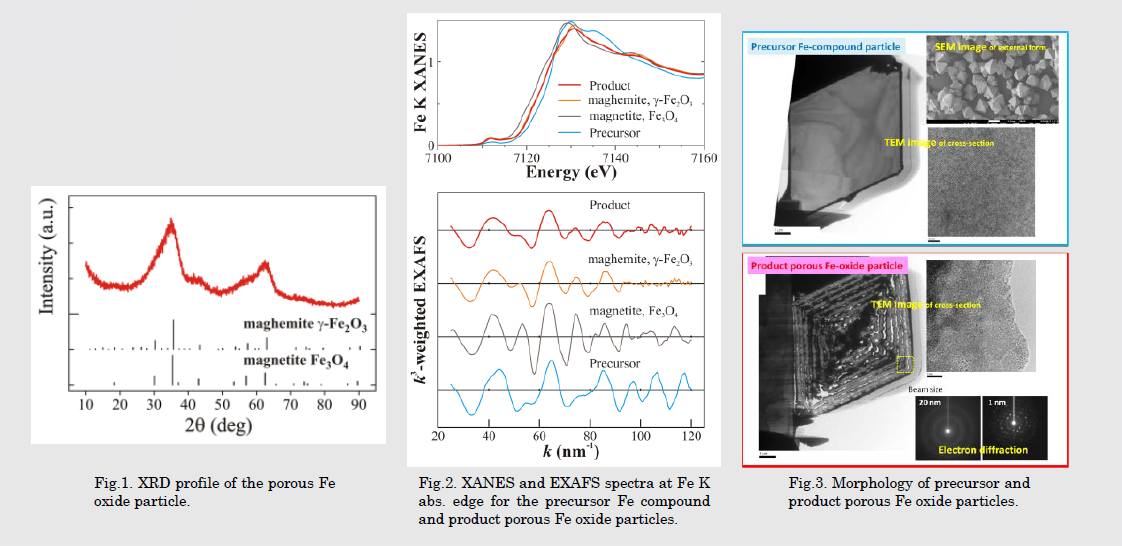
新しい作製法による大比表面積多孔質磁性酸化鉄粒子の開発を進めており、交流磁場誘起発熱という物理的作用で脱離・濃縮回収できるシステム構築を目指しています。目標達成のため、吸・脱着特性向上とともに粒子内空隙デザイン最適化や局所構造最適化、そして磁気特性最適化を目指して吸着材開発を推進しています。
The development of the magnetic iron oxide particles with large particle size, large specific surface area, and large pore and void volume as adsorbent material by using novel liquid phase reaction process has been investigated. The aim is establishment of a system with high efficiency in desorption and condensation recovery for the physical thermo-effect induced by applied alternating magnetic field. The optimization of void design, local structure and magnetic properties for suitable adsorbent material have been promoted as well as the progress of adsorption-desorption characteristics.
研究図Research Figure
文献 / Publications
Mater. Trans. 50, 1196 (2009), High Temp. Mater. Proc. 31, 451 (2012)
研究者HP
- kozo.shinoda.e8
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - http://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/suzuki/