
RIES
Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University
北海道大学
電子科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2017/02/25
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name石旭 Xu SHI
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Affiliation北海道大学 電子科学研究所
グリーンナノテクノロジー研究センター
Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University
Green Nanotechnology Research Center -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords局在プラズモン
人工光合成
光電気化学
半導体薄膜
Plasmonics
Artificial photosynthesis
Photochemistry
Semiconductor thin film
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
薄膜を用いたプラズモニックソーラーエネルギー変換システムの開発
Development of novel plasmonic thin-film photoelectrochemical solar energy conversion system
研究の背景 Background of the Research
低炭素社会を実現するためには、持続可能な再生可能エネルギーの利用が不可欠である。安価で地球に豊富にある材料を用いた人工光合成系の構築は、太陽エネルギーを化学エネルギーに変換する最も有望な方法の一つである。光電気化学セルを用いたソーラーエネルギー技術の開発は人工光合成系構築のための重要な研究分野である。
In order to achieve the low carbon societies, it is imperative to develop sustainable renewable energy to meet the global energy demand while reducing carbon dioxide emissions. Solar fuel generation using inexpensive, earth-abundant materials is one of the most promising renewable energy source to convert solar energy to chemical energy that can be stored and used on demand. Photoelectrochemical solar cell (PEC) that can generate both electrical and electrochemical energy is an important research field for the solar to fuel energy conversion.
研究の目標 Research Objective
本研究の目的はプラズモン金属ナノ粒子を用いた革新的な広波長域応答薄膜ソーラーエネルギー技術を開発することである。具体的には、金属ナノ粒子/半導体界面において効率的な電荷分離ヘテロ接合を開発し、プラズモン金属ナノ粒子アンテナによる光閉じ込め機能をさらに増強し、革新的なプラズモン薄膜エネルギー変換システムの実現を目指す。
The main research objective is to construct a broadband photoelectrochemcial thin-film solar cell for solar fuel generation by employing novel plasmonic metal nanoparticles. Significant attention is focused on the developing of an efficient charge separation heterojunction at metallic nanoparticles/semiconductor interface, and establishing a novel method to construct a broadband, super light absorption plasmonic ultra-thin-film system for efficient solar fuel generation.
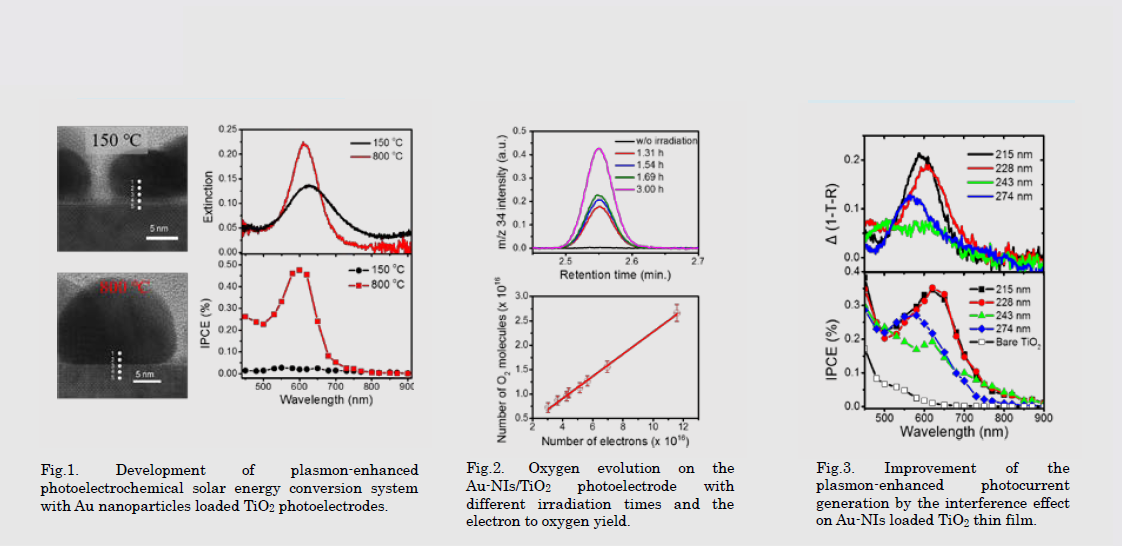
研究図Figures
論文発表 / Publications
Interface Focus, 5, 20140082 (2015). Angwe. Chem. Int. Ed., 53, 10350 (2014). J. Phys. Chem. C, 117 2494 (2013). J. Phys. Chem. C, 117 24733 (2013).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- shixu
 es.hokudai.ac.jp
es.hokudai.ac.jp - http://misawa.es.hokudai.ac.jp