
IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2022/08/30
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name濵口祐 Tasuku HAMAGUCHI
准教授 Associate Professor -
所属
Affiliation東北大学 多元物質科学研究所
有機・生命科学研究部門 生物分子機能計測研究分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Division of Organic- and Bio-materials Research, Nano Biophysics -
研究キーワード
Research Keywordsクライオ電子顕微鏡
単粒子構造解析
電子線トモグラフィー
膜タンパク質
Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM)
Single-particle structural analysis
Tomography
Membrane proteins
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
高分解能単粒子構造解析を用いた生体分子の可視化
Visualization of biomolecules using high-resolution single-particle structural analysis
研究の背景 Background of the Research
クライオ電子顕微鏡は生体分子を固定することなく観察できるパワフルな手法で2017年にノーベル賞を受賞している.近年ではタンパク質の構造解析においてX線結晶構造解析に迫る1Å台前半の分解能で構造決定された報告もされており,その需要はますます高まっている.また,単粒子構造解析だけにとどまらず,クライオ電子線トモグラフィーや電子線回折など多様な構造解析にも対応可能である.
Cryo-EM is a powerful technique that allows observation of biomolecules without fixation, and was awarded the Nobel Prize in 2017. In recent years, there have been reports of protein structures determined at resolutions in the low 1Å range, which is comparable to X-ray crystallography, and the demand for cryo-EM is increasing. In addition to single-particle structure analysis, the cryo-EM can also be used for cryo-electron tomography, electron diffraction, and a variety of other structural analyses.
研究の目標 Research Objective
本研究では,膜タンパク質や電子顕微鏡が苦手とする小さなタンパク質について,高分解能構造解析を目的とする.これらタンパク質には創薬ターゲットなどが多く含まれており,医療分野への寄与も期待できる.また,生体分子の高精度構造解析を達成するだけでなく,クライオ電子顕微鏡をより幅広い試料へと適用する.
We aim at high-resolution structural analysis of membrane proteins and small proteins that are difficult to analyze with electron microscopy. These proteins contain many drug targets and are expected to contribute to the medical field. In addition to achieving high-precision structural analysis of biomolecules, we will also apply cryo-EM to a wider range of samples.
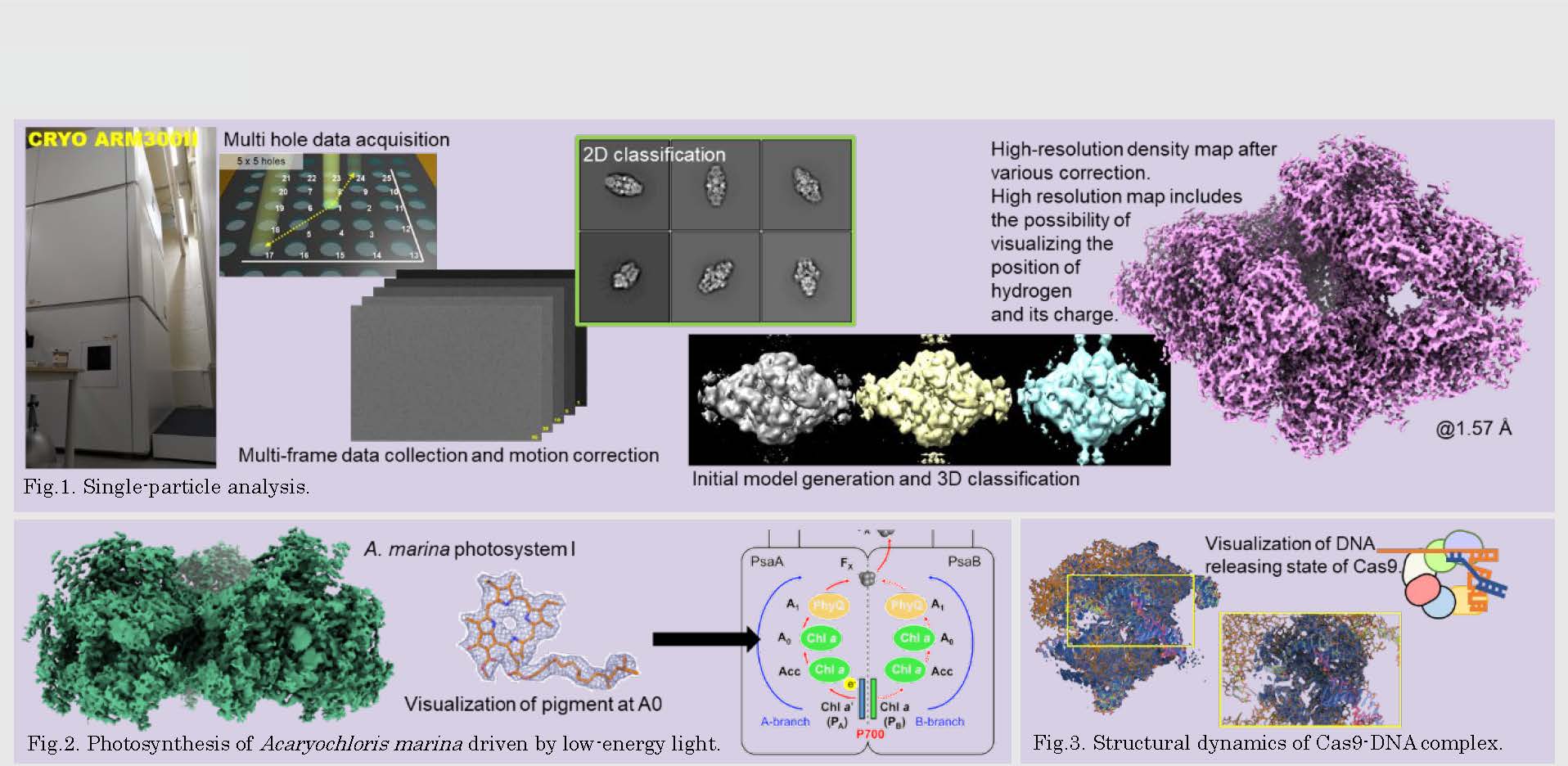
研究図Figures
論文発表 / Publications
Nature commun. in press (2022), eLife 11 (2022), Nature Commun. 12 (2021), BBA 1862 (2021), Commun. Biol. 4 (2021), Commun. Biol. 3 (2020), J. Struct. Biol. 209 (2020), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 366 (2019), J. Struct. Biol. 207 (2019)
研究者連絡先 / HP
- tasuku.hamaguchi.c3
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - https://www.lifesci.tohoku.ac.jp/research/fields/laboratory.html?id=45416