
IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2025/05/30
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name押切友也 Tomoya OSHIKIRI
准教授 Associate Professor -
所属
Affiliation東北大学 多元物質科学研究所
マテリアル・計測ハイブリッド研究センター 光機能材料化学分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Materials-Measurement Hybrid Research Center, Photo-Functional Material Chemistry -
研究キーワード
Research Keywordsプラズモン
量子コヒーレンス
モード結合
メタサイト
Plasmon
Quantum coherence
Modal coupling
Metasite
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
ナノ構造精密加工による近接場制御と人工光化学反応場:メタサイトの創製
Control of near field and creation of artificial photochemical reaction field: metasite
研究の背景 Background of the Research
ナノサイズの金属や誘電体は光と共鳴して、その近傍に近接場と呼ばれる局在電場を形成する。近年、微細構造加工技術の劇的な進歩に伴い、ナノ構造を精密に設計・作製することでナノ空間での光を自在に制御することが可能となった。近接場の光による新たな光化学反応への応用が期待されており、特に太陽光中の可視・近赤外光を有効利用可能な方法論として注目されている。
Nanostructures of metal and dielectric materials resonate with visible light and induce a local electric field, which is called as the near field. Recently, significant improvements in nanofabrication technology enables the precise design and arbitrary control of the light in the near field. Near-field photonics is expected to be a strong methodology to achieve a novel chemical reaction driven by the visible to infrared wavelength region of sunlight.
研究の目標 Research Objective
本研究では、精密に作製されたナノ構造体の形状とその配列が形成するナノ空間の光化学反応場(メタサイト)において新規化学反応を探索する。特に、プラズモンやMie共鳴体といった粒子状の共鳴体と他の光共振器との強い相互作用(モード結合)が示す量子コヒーレンスを用い、メタサイトでの統合的な近接場の制御と光-物質相互作用への応用を行う。本研究は、キラル近接場における物質変換や、人工光合成反応をはじめとした光-化学エネルギー変換システムの実用化に貢献可能である。
This study explores new chemical reactions in the photochemical reaction fields formed by the shapes and arrangements of precisely fabricated nanostructures (metasites). We will use the quantum coherence exhibited by modal coupling between particle resonators, such as plasmons and Mie resonators, and other optical cavities to control the near field on the metasite. This research contributes to the practical application of material conversions in helical near field and artificial photosynthesis reactions on metasite.
研究図Figures
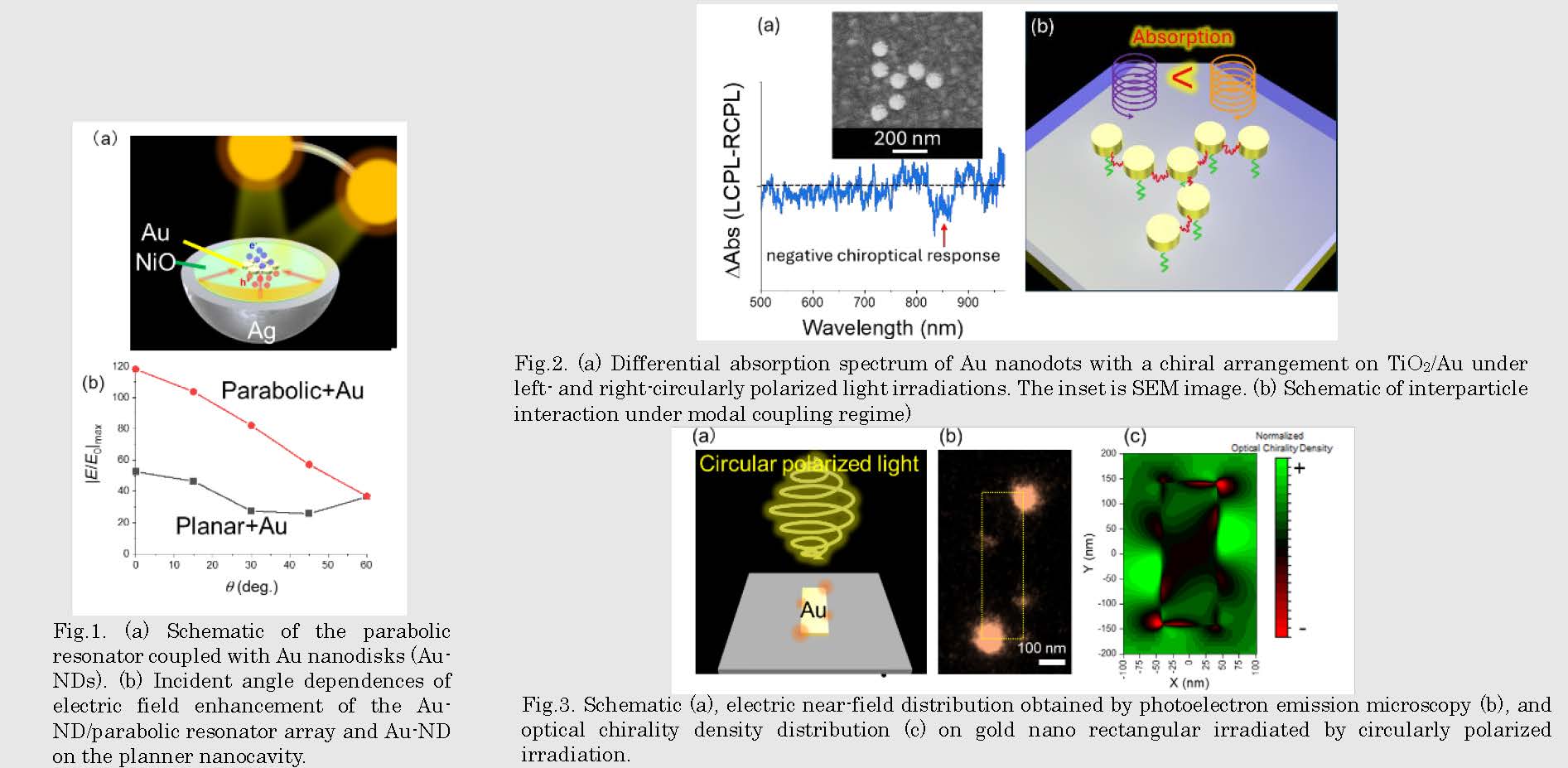
Fig.2. Near-field and phase distributions of the 37 Au-NDs with (a, b, e, f) and without (c, d, g, h) parabolic resonator array. (a, c, e, g) linearly polarized excitation. (b, d, f, h) circularly polarized excitation.
Fig.3. Schematic (a), electric near-field distribution obtained by photoelectron emission microscopy (b), and optical chirality density distribution (c) on gold nano rectangular irradiated by circularly polarized irradiation.
論文発表 / Publications
Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 24, 13 (2025). J. Phys. Chem. C., 128, 5271 (2024). ACS Nano, 8, 4993 (2024). ACS Nano, 17, 8315 (2023). Chem. Eur. J., 28, e202200288 (2022). ACS Nano, 15, 16802 (2021). Nat. Nanotechnol., 13, 953 (2018). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 3942 (2016).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- tomoya.oshikiri.c1
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - http://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/nakagawa/