
SANKEN
The University of Osaka
大阪大学
産業科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2019/08/08
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name岡本一将 kazumasa OKAMOTO
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Affiliation大阪大学 産業科学研究所
量子ビーム物質科学研究分野
SANKEN, The University of Osaka
Department of beam materials science -
研究キーワード
Research Keywordsリソグラフィ
レジスト材料
量子ビームプロセス
Lithography
Resist materials
Quantum beam process
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
量子ビームプロセス機構の解明と高度化
Elucidation and improvement of quantum beam process mechanism
研究の背景 Background of the Research
電子線、X線やレーザー光などの量子ビームは、物質に照射することにより、様々な化学・物理的作用を起こします。半導体量産用レジスト材料をはじめとする有機・無機物質に量子ビームを照射することによって生じる反応機構の解明は、材料の高性能化につながることから重要な課題となっています。
Quantum beam such as electron beam, X-ray, and laser light cause various chemical and physical effects on irradiating materials. Elucidating the reaction mechanism that occurs by quantum beam irradiations to organics and inorganics such as resist materials for mass production of semiconductor devices is an important issue, because it leads to the enhancement of material performance.
研究の目標 Research Objective
レジストをはじめとする種々の機能性を有する材料の放射線化学反応を明らかにすることによって、それらの性能を向上できる新規プロセスや材料の化学組成を探索し、極端紫外線(EUV)や電子線といった量子ビームを用いた半導体量産用極微細加工を始めとするナノプロセスの発展・高度化を目指しています。
By clarifying the radiation chemical reactions of various functional materials, we seek new processes and chemical compositions of materials in order to improve their performance. And, we investigate the nanoprocesses such as ultra-fine processing for semiconductor mass production using quantum beam such as extreme ultraviolet (EUV) and electron beam to enhance the performances.
研究図Figures
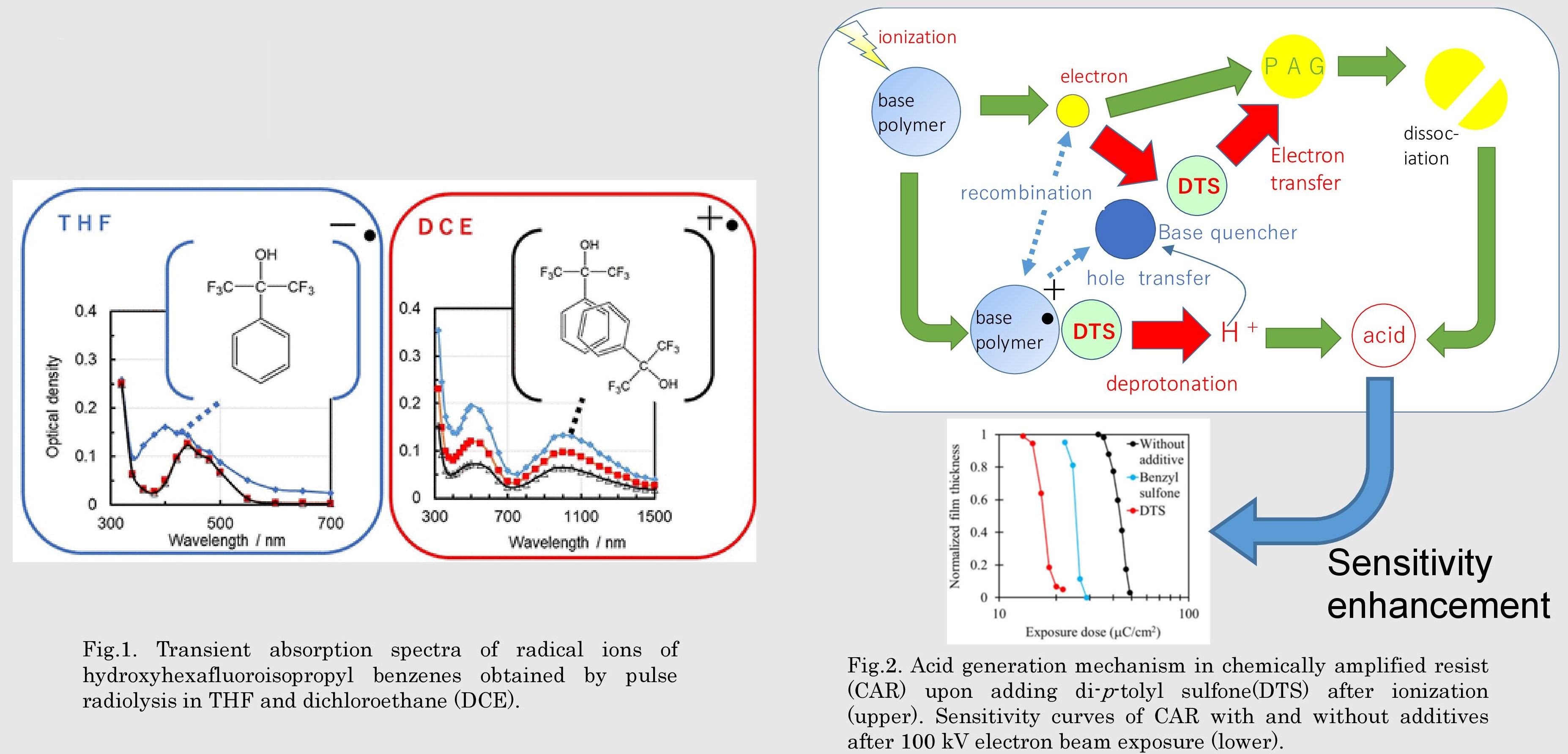
Fig.2. Acid generation mechanism in chemically amplified resist (CAR) upon adding di-p-tolyl sulfone(DTS) after ionization (upper). Sensitivity curves of CAR with and without additives after 100 kV electron beam exposure (lower).
論文発表 / Publications
J. Phys. Chem. A,121(49), 9458 (2017)., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 56, 06GD01 (2017)., Sci. Rep., 8, 177(2018).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- kazu
 sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp
sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp - https://www.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/labs/bms/