CLS
Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology
東京工業大学
科学技術創成研究院
化学生命科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2022/09/07
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name安田貴信 Takanobu YASUDA
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Professional Affiliation東京工業大学科学技術創成研究院化学生命科学研究所
分子生命化学領域
Laboratory for Chemistry and Life Science, Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Division of Molecular Bioscience -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords抗体工学
ペプチド工学
バイオセンサー
Antibody engineering
Peptide technology
Biosensor
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
蛋白質・ペプチド工学的手法に基づくバイオセンサーの創出
Development of biosensor based on protein and peptide engineering methodologies
研究の背景 Background
抗体と抗原の特異的な結合を利用した標的物質の測定法である免疫測定法は、生体物質や非生体物質を問わず混合物中に存在する微量物質を選択的に検出・定量することができます。そのため、生物学研究から臨床診断、食品の衛生管理、環境保全など、様々な分野において不可欠な方法論となっています。その一方で、現在普及している免疫測定法には測定時間や感度の面で改善の余地があり、より良い測定法の開発を目指して世界中で日夜研究が行われています。
Immunoassay is a method of measuring target substances taking advantage of specific binding ability of antibodies. It can selectively detect and quantify trace substances present in a biological sample. Therefore, immunoassay is an indispensable methodology in various fields ranging from biological research to clinical diagnosis, food sanitation, and environmental conservation. On the other hand, there is room for improvement in terms of measurement time and sensitivity in the immunoassay methods.
研究の目標 Outcome
私たちは抗体を基盤とし、ペプチドや発光酵素を組み合わせて生体試料や環境試料に含まれる微量物質を簡単に検出できるバイオセンサーの開発を行っています。ファージを用いた抗体の分子進化や計算科学的手法を取り入れて実用的な感度のセンサーとなるよう作り込み、病気のマーカーやウイルスを従来よりも簡便かつ高感度に検出できるツールとして社会実装することが目標です。
We are developing antibody-based biosensors that can easily detect trace substances in biological and environmental samples by combining peptides and luminescent enzymes. Our goal is to create a biosensor with practical sensitivity by using molecular evolution methods (e.g. phage display) and computational methods, and to implement it in society as a tool that can detect disease markers and viruses easily and with high sensitivity.
研究図Research Figure
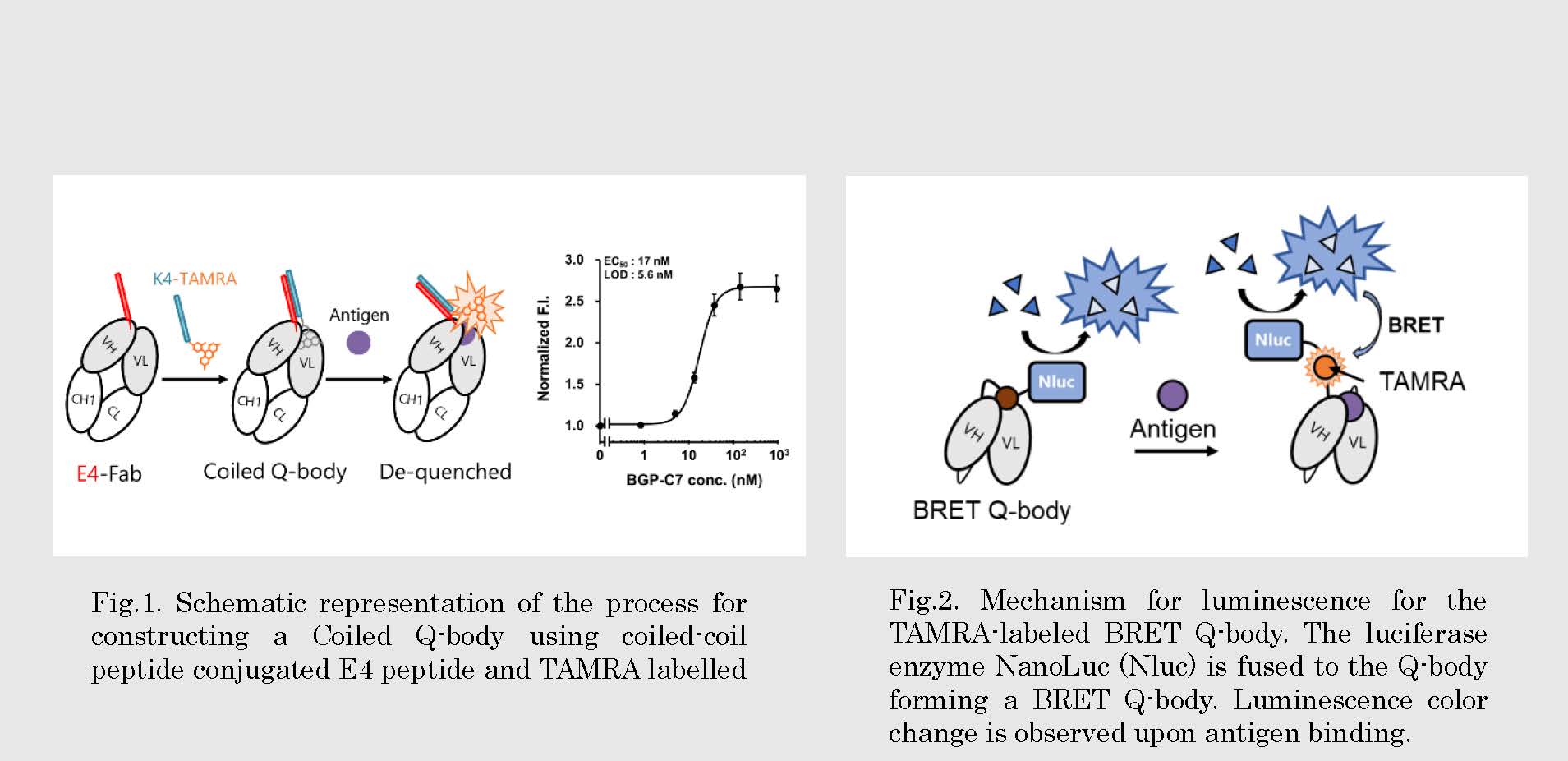
Fig.2. Mechanism for luminescence for the TAMRA-labeled BRET Q-body. The luciferase enzyme NanoLuc (Nluc) is fused to the Q-body forming a BRET Q-body. Luminescence color change is observed upon antigen binding.
文献 / Publications
Chem. Commun. 57, 8206-8209 (2021). Anal. Chem. 93, 21, 7571-7578 (2021).
研究者HP
- yasuda.t.af
 m.titech.ac.jp
m.titech.ac.jp - http://www.ueda.res.titech.ac.jp/