IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/05/02
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name吉松公平 Kohei YOSHIMATSU
准教授 Associate Professor -
所属
Professional Affiliation東北大学多元物質科学研究所
無機材料研究部門 ナノ機能物性化学研究分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Division of Inorganic Material Research, Nano Physical Chemistry -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords酸化物薄膜
金属絶縁体転移
超伝導
Oxide thin films
Metal-insulator transition
Superconductivity
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
酸化物薄膜を用いた新奇物性開拓
Development of unique physical properties in oxide thin films
研究の背景 Background
遷移金属酸化物は高温超伝導や巨大磁気抵抗などの特異な物性が発現します。これら物性を活用し実社会へと応用することで、情報化社会のさらなる発展やエネルギー・環境問題の解決が可能となります。材料の形状に薄膜を選択することで、バルク体では不可能な新規物性の開拓や制御が可能となり、遷移金属酸化物の持つポテンシャルを最大限に引き出すことができます。
Transition-metal oxides exhibit unique properties such as high-temperature superconductivity and giant magnetoresistance. Application of the properties enables us to further develop information society and solve energy and environmental issues. The properties can be developed and controlled using thin-film form, resulting that it is possible to maximize the potentials of transition-metal oxides beyond bulk materials.
研究の目標 Outcome
酸化物薄膜の合成にはパルスレーザ堆積法を用いています。また、合成した薄膜に対してさらなる加工・化学反応を行うことで薄膜特有の物性開拓を行っています。具体的には(1) 高品質な単結晶薄膜ヘテロ構造の形成、(2) 化学反応等を利用した新規物性の創生と制御、(3) 放射光光源を用いた電子状態観測、を主な手法として研究を進めています。
Pulsed-laser deposition technique is utilized to obtain oxide thin films. Experimental studies on the following subjects have been performed in order to achieve the research subjects: (1) fabrication of high-quality single crystalline oxide films and heterostructures, (2) Creation and control of unique physical properties induced by chemical reactions, and (3) observation of electronic structures using synchrotron spectroscopy.
研究図Research Figure
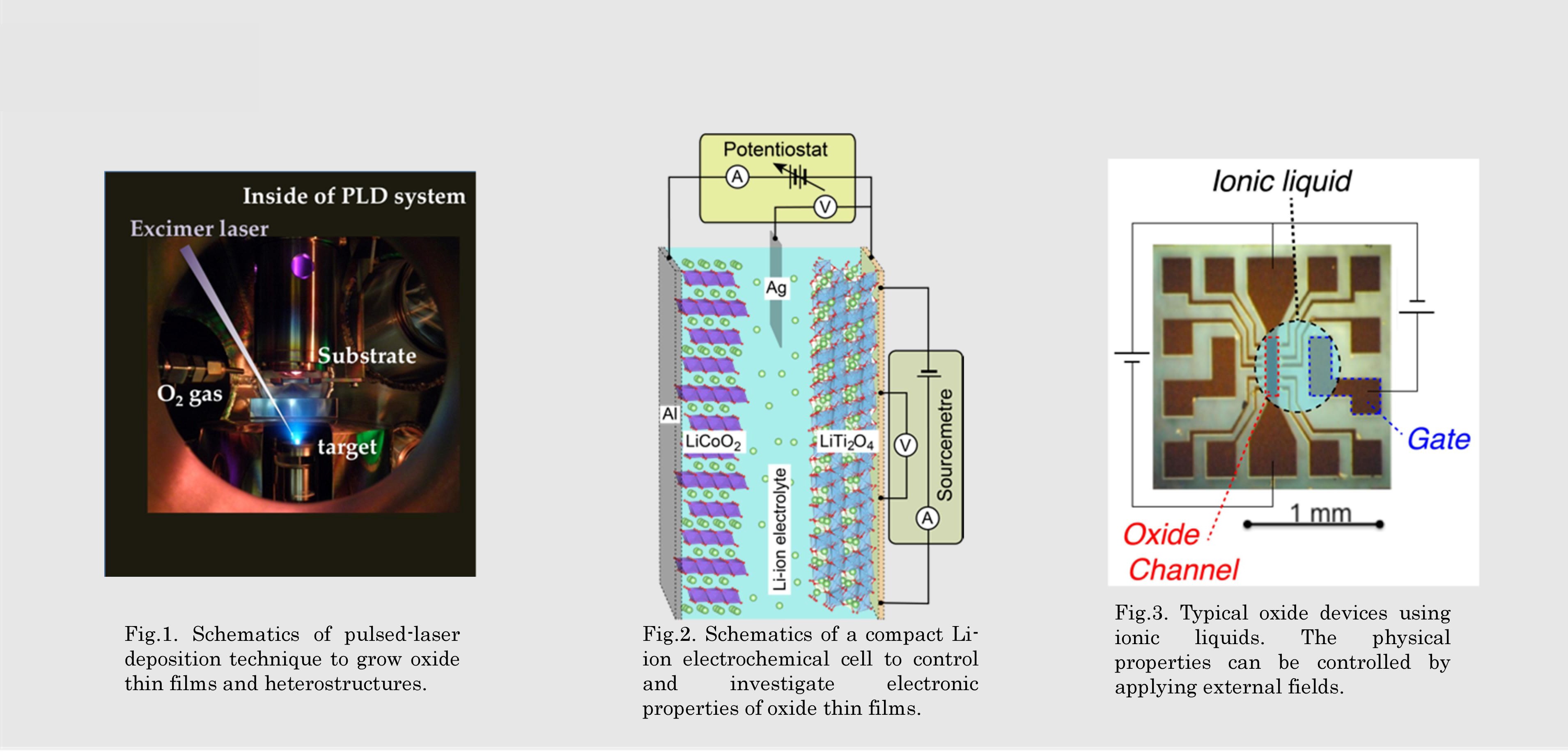
Fig.2. Schematics of a compact Li-ion electrochemical cell to control and investigate electronic properties of oxide thin films.
Fig.3. Typical oxide devices using ionic liquids. The physical properties can be controlled by applying external fields.
文献 / Publications
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 88, 035001 (2019). Phys. Rev. Mater. 2, 115003 (2018). APL Mater. 6, 101101 (2018). Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 232103 (2018). npj QuantumMaterials 3, 3 (2018). Sci. Rep. 7, 12544 (2017). J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 18717 (2017). Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 162101 (2017). Phys. Rev. B 93, 195159 (2016).
研究者HP
- kohei.yoshimatsu.c6
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - http://sites.google.com/site/koheiyoshimatsuhpjpn/home