
IMCE
Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University
九州大学
先導物質化学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/06/09
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name井原史朗 Shiro IHARA
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Affiliation九州大学 先導物質化学研究所
融合材料部門 ナノ材料解析分野
Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University
Division of Integrated Materials, Nanoscale Characterization of Materials -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords機械学習
電子顕微鏡
転位
Machine Learning
Electron Microscope
Dislocation
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
機械学習を用いた顕微鏡像の高精度化およびその場観察への応用
Improving microscopic images and application for in-situ experiments by machine-learning
研究の背景 Background of the Research
電子顕微鏡による観察は材料の研究で欠かせませんが,その場観察で必要となる高速撮像を行うと像に含まれるノイズが大きくなり,高精細像との両立はハードウェアの観点からでは困難です.高い時間・空間分解能を有する観察技術を開発することで,外部応力下や加熱時の転位運動を始めとした幅広い現象を顕微鏡によってより詳細に捉えることが可能となります.
Electron microscope is widely used in material research. The major but hard to solve problem of the device is how to denoise images taken by high speed operation. Developing the observation technic having high spatial-temporal resolution could lead to analysis of broader range of phenomena such as dislocation motion under external stress and heating environment.
研究の目標 Research Objective
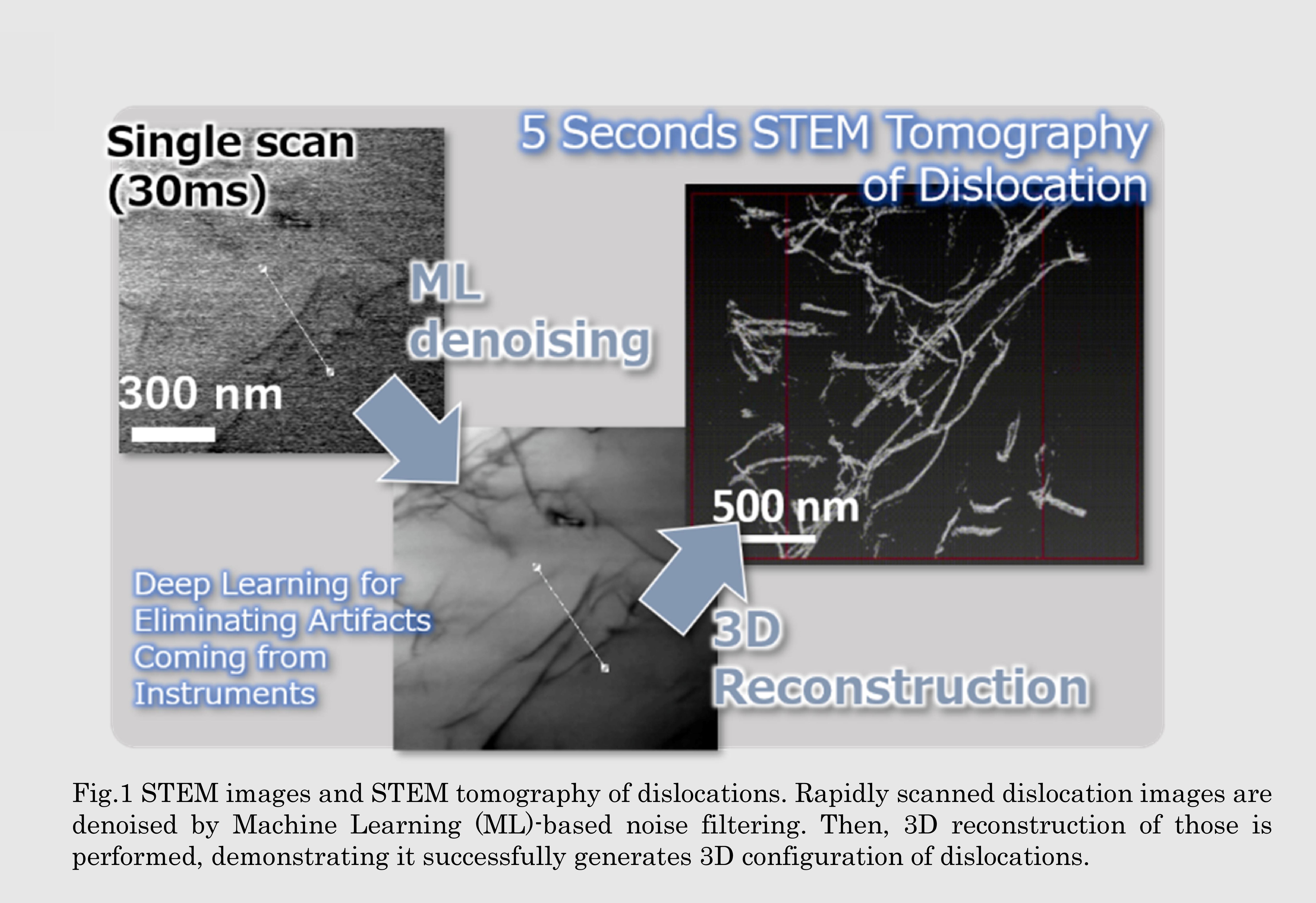
機械学習による画像のノイズ除去を試みています.STEMによって高速撮像した転位像に対して,同一視野で取得したノイズの少ない転位像を学ばせることで高精度な像が得られる画像フィルタを開発しています.STEMはTEMに比べてより厚みのある試料を扱えることから,このような画像フィルタによって転位の構造を詳細に捉えられることができ,その場観察と組み合わせることで種々の刺激に対する転位の運動を明らかにできることが期待できます.
Machine learning (ML) based noise filtering to rapidly scanned STEM images of dislocation has been shown to precisely denoise the images. Applying this denoise technic to in-situ observation of dislocations could reveal dislocation motions against various stimuli in accurate manner.
研究図Figures
論文発表 / Publications
Y. Zhao, S. Koike, R. Nakama, S. Ihara, M. Mitsuhara, M.Murayama, S. Hata and H. Saito,”Five-second STEM dislocation tomography for 300 nm thick specimen assisted by deep-learning-based noise filtering”, Nat. Commun. (投稿中)
研究者連絡先 / HP
- ihara-shiro
 cm.kyushu-u.ac.jp
cm.kyushu-u.ac.jp - https://murayamasaito.weebly.com/