
IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/05/03
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name藤田伸尚 Nobuhisa FUJITA
講師 Lecturer -
所属
Affiliation東北大学 多元物質科学研究所
無機材料研究部門 金属機能設計研究分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Division of Inorganic Material Research, Metallurgical Design for Material Functions -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords準結晶
近似結晶
クラスタ
X線回折
構造解析
準周期タイリング
擬ギャップ
熱電物性
Quasicrystal
periodic approximant
cluster
X-ray diffraction
structure analysis
quasiperiodic tiling
pseudo-gap
thermoelectric properties
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
準結晶化合物の新規創出とその構造・機能の探求
Creation of novel quasicrystalline compounds and exploration of their structure and functions
研究の背景 Background of the Research
準結晶は非周期性と長距離秩序を併せ持つ固体物質であり,適切な合金組成において自発的に生成する金属間化合物として数多く見いだされている.正二十面体準結晶は正二十面体対称クラスタによる空間充填構造として理解され,クラスタ同士が互いに原子を共有しながら結合しそれらが準周期的に配列したものと考えられる.一方,準結晶の組成近傍で生成する近似結晶は,単位胞が非常に大きく準結晶に対する周期近似として理解できる.準結晶や近似結晶の物性は,その構造的複雑性に起因して通常の(単位胞の小さい)結晶とは大きく異なる.
Quasicrystals are solid-state materials that lack periodicity but maintain long-range order. They often exist as intermetallic compounds with appropriate compositions. Icosahedral quasicrystals are based on icosahedral clusters, which arrange themselves in a quasiperiodic manner. Periodic crystals with large unit cells, having similar compositions to those of quasicrystals, are referred to as periodic approximants. Both quasicrystals and periodic approximants exhibit unique physical properties associated with their complex structures.
研究の目標 Research Objective
アルミニウムとパラジウムをベースとした合金に鉄やクロム等の様々な遷移金属を加えることで,様々なタイプの準結晶および近似結晶が生成可能である [1,2].本研究では,新しい遷移金属を組み合わせることで準結晶や近似結晶を新たに創出する.また,X線回折を用いた構造解析[1]や物性測定[3]を行うことで,元素の組み合わせによる構造形成や物性への影響を系統的に調べる.既に,遷移金属の組み合わせによりフェルミ準位近傍の擬ギャップの深さが制御できる可能性が示唆されており[3],このことを応用した熱電物性等の機能開拓を進める.
Various types of quasicrystals and periodic approximants can be produced by adding transition metals such as iron and chromium to alloys based on aluminum and palladium [1,2]. Our aim is to create novel quasicrystals and periodic approximants using various combinations of metallic elements. We will also investigate systematic trends in structure formation and physical properties through X-ray structural analysis [1] and physical property measurements [3]. It has already been suggested that the combination of elements can control the depth of the pseudo-gap near the Fermi level [3], prompting us to exploit these materials for future thermoelectric applications.
研究図Figures
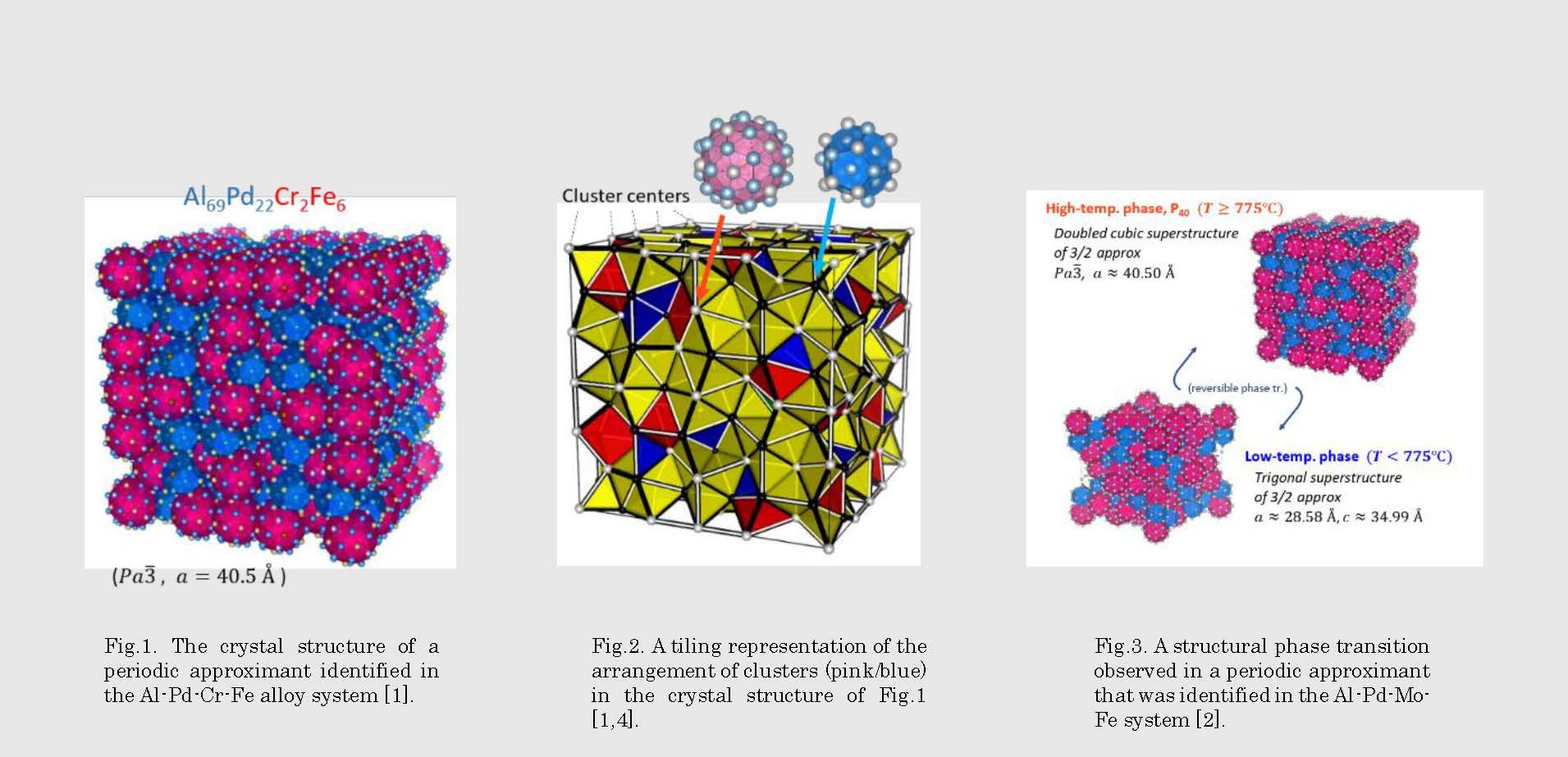
Fig.2. A tiling representation of the arrangement of clusters (pink/blue) in the crystal structure of Fig.1 [1,4].
Fig.3. A structural phase transition observed in a periodic approximant that was identified in the Al-Pd-Mo-Fe system [2].
論文発表 / Publications
[1] N. Fujita, H. Takano, A. Yamamoto, and A.-P. Tsai, Acta Cryst. A 69 (2013) 322.
[2] N. Fujita and M. Ogashiwa, Mater. Trans. 62 (2021) 329.
[3] S. Sarkar, P. Sadhukhan, V. K. Singh, A. Gloskovskii, K. Deguchi, N. Fujita, and S. R. Barman, Phys. Rev. Res. 3 (2021) 013151.
[4] N. Fujita, M. Mihalkovič, and C. L. Henley, Isr. J. Chem., early view, DOI: 10.1002/ijch.202300130.
研究者連絡先 / HP
- nobuhisa.fujita.a4
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - https://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/kameoka/html/fujita-nobuhisa/