
IMCE
Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University
九州大学
先導物質化学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2017/02/25
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name久保木タッサニーヤー Thasaneeya KUBOKI
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Affiliation九州大学 先導物質化学研究所
医用生物物理化学分野
Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University
Laboratory of Biomedical and Biophysical Chemistry -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords分子生物学
遺伝子工学
材料物性学
細胞運動
幹細胞操作
Molecular Biology
Genetic Engineering
Biomaterials
Cell migration
Stem cell manipulation
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
細胞運動性を制御するメカノバイオマテリアルを開発する。
Development of mechano-biomaterials for cell manipulation.
研究の背景 Background of the Research
Mechanobiology is an emerging research science that use the integrated knowledge from medical, engineer, cell biology and biomechanics fields to explain how the mechanical signal from cellular microenvironment could regulate the cell functions. We are seeking to understand the mechanism governing normal physiology/pathological conditions of the living cells by developing mechanical substrates to control the cell behaviors such as their directional migration, proliferation or differentiation. Elasticity tunable hydrogenous gelatin gel for cell manipulation is being developed using photocurable styrenated gelatin. The mechanism of cell-substrate interaction is being investigated using molecular biology and biochemistry approaches.
研究の目標 Research Objective
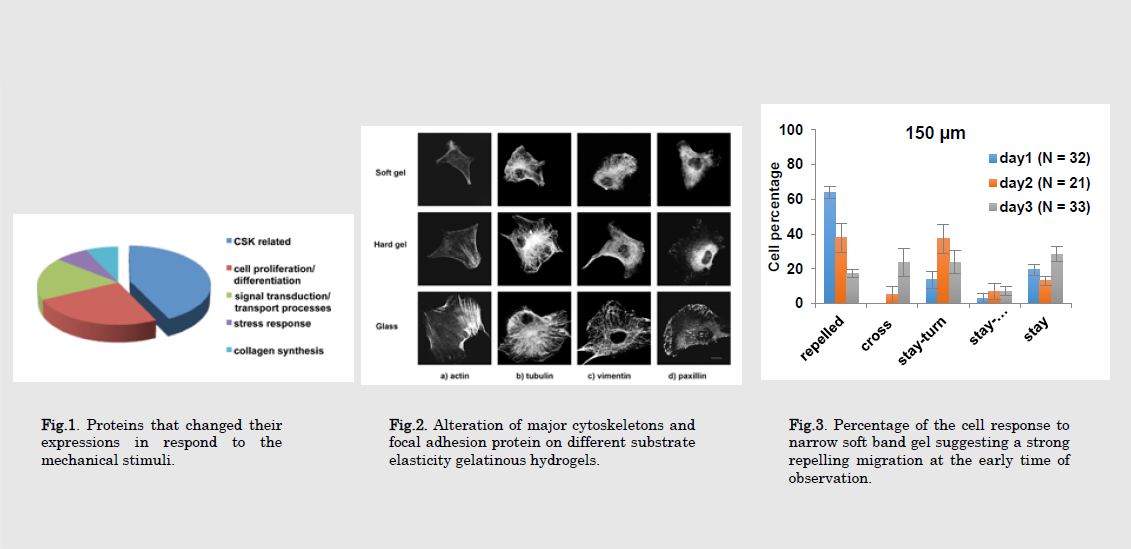
In tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, stem cell is expected to be one of the potential sources for future cell based therapeutic strategies. Our research focuses on the analysis of MSC proteome on gels with different stiffness using 2 dimensional differential in gel analysis. We achieved in demonstrating the significant changes of the major cytoskeketon and other signaling proteins in respond to substrate elasticity. This finding provided significant impact on the designing of biomaterials to control stem cell fate. For the aspect of cell migration, we successfully fabricated the soft band patterned gels that induced a strong mechanorepellent effect on cell migration. This mechanical substrate is useful for the future development of cell separation devices based on the variability in the mechanical responsiveness of the different cell types.
研究図Figures
論文発表 / Publications
Cell Struct Funct. 2012;37(2):127-39, Langmuir 2014; 30, 6187-6196
研究者連絡先 / HP
- kubokit
 ms.ifoc.kyushu-u.ac.jp
ms.ifoc.kyushu-u.ac.jp - http://www.cm.kyushu-u.ac.jp/mbbmc_imce_new/