
IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/05/03
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name亀岡聡 Satoshi KAMEOKA
教授 Professor -
所属
Affiliation東北大学 多元物質科学研究所
無機材料研究部門 金属機能設計研究分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Division of Inorganic Material Research, Metallurgical Design for Material Functions -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords触媒材料
合金触媒
金属・酸化物コンポジット
Catalytic materials
Alloy catalyst
Metal-oxide composite
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
新奇金属・合金触媒材料の設計と調製
Research and development of novel metallic materials for catalysis
研究の背景 Background of the Research
来るカーボンニュートラル社会を実現するためのキーマテリアルの1つとして触媒がある。触媒材料に対するニーズは益々高まってきており、特に最近、脱貴金属化や貴金属代替合金触媒の開発が重要課題の一つとなっている。しかし、金属や合金は触媒材料としてよく用いられているにもかかわらず、驚くことにこれまで金属学の視点で触媒機能を扱った研究は非常に少なく系統的に金属・合金触媒材料の設計・開発は行なわれていない。
Catalyst is one of the key materials for realizing a decarbonized society. In recent years, precious metal–free and development of precious metal alternative alloy catalysts have become the most important issues. However, very few researches on catalytic materials have been performed from the view point of metallurgy so far.
研究の目標 Research Objective
我々は、優れた触媒機能を持つ合金触媒を設計・調製するために金属学に基づく金属ナノ組織制御法を開拓し、新たな触媒機能創出ならびに触媒材料開発を行っている。金属・合金自身はもとよりこれらをプラットフォームあるいは触媒前駆物質として扱い、合金の組織制御、選択的溶出処理あるいは酸化・還元処理などを組み合わせることで、従来の触媒調製法では実現できないユニークな複相合金組織・形態と触媒機能(活性、選択性、熱安定性)を有する新奇合金触媒材料を創製する。
We have fabricated novel catalysis materials from well-defined materials such as intermetallic compounds and spinel oxides etc. These well-defined materials are promising precursors for leaching or reduction for the fabrication of self-assembled nanoarchitecture and for obtaining porous catalysis materials. Novel catalytic materials with high catalytic performance are designed from microstructural tailoring based on metallurgy.
研究図Figures
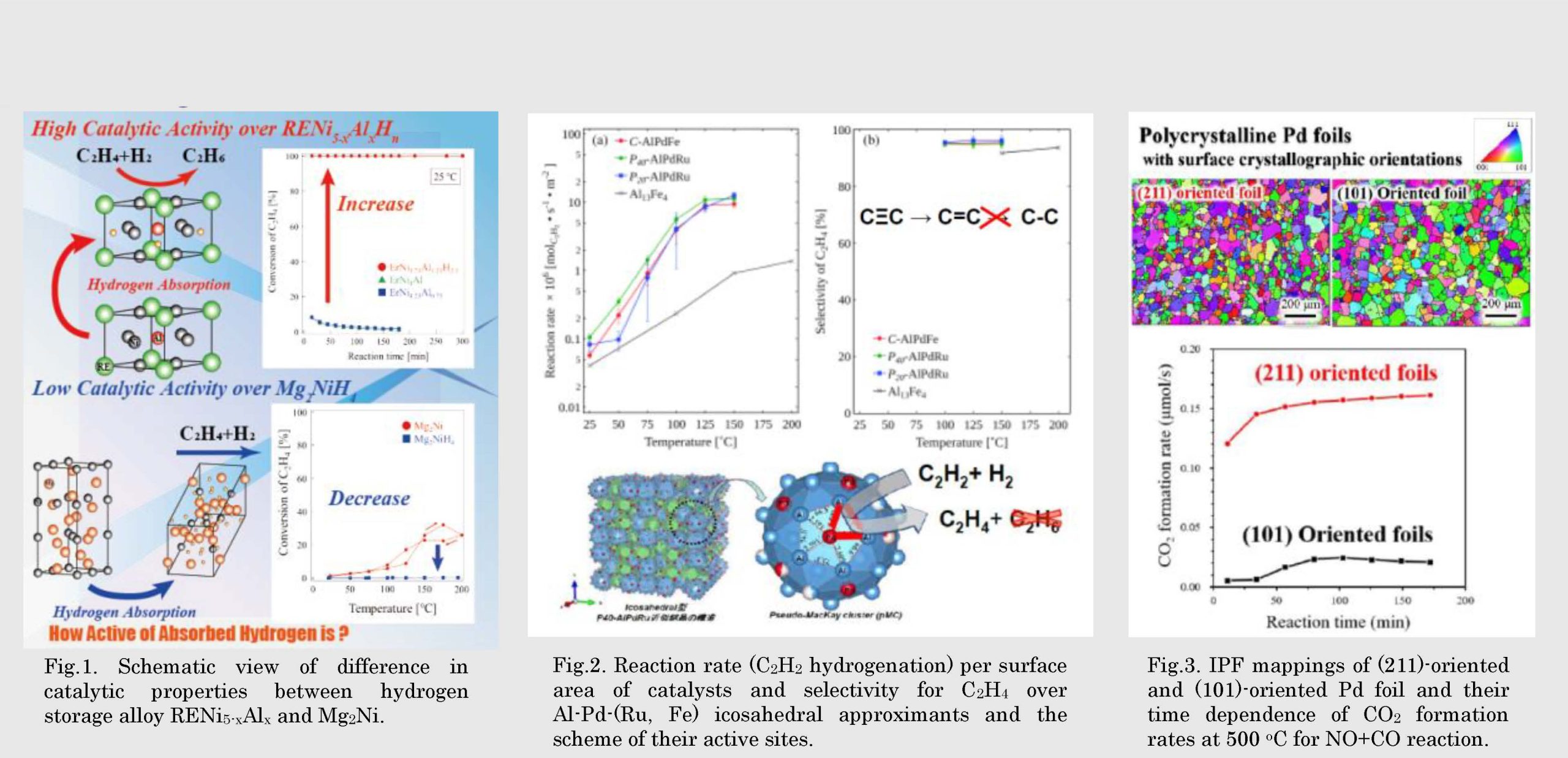
Fig.2. Reaction rate (C2H2 hydrogenation) per surface area of catalysts and selectivity for C2H4 over Al-Pd-(Ru, Fe) icosahedral approximants and the scheme of their active sites.
Fig.3. IPF mappings of (211)-oriented and (101)-oriented Pd foil and their time dependence of CO2 formation rates at 500 oC for NO+CO reaction.
論文発表 / Publications
Appl. Catal. A 569, 101 (2019). Carbon 147, 154 (2019). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45, 19226 (2020). J. Phys. Chem. C 125, 20919 (2021). RSC Advances 11, 15296 (2021). Mater. Trans. 62, 1089 (2021). J. Solid State Chem. 309, 122984 (2022). Mater. Trans. 64, 2440 (2023). Ceramics Int. 50, 8907 (2024).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- satoshi.kameoka.b4
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - https://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/kameoka/