RIES
Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University
北海道大学
電子科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2017/02/25
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name西村吾朗 Goro NISHIMURA
助教 Assistant Professor -
所属
Professional Affiliation北海道大学電子科学研究所
社会創造数学研究センター
Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University
Research Center of Mathematics for Social Creativity -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords医用生体光学
拡散光イメージング・拡散相関分光法・蛍光ゆらぎ分光法
拡散光画像再構成
時間領域単一光子検出法
Diffuse optical tomography and diffuse correlation spectroscopy
Fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy
Image reconstruction in a diffusion system
Time-domain single photon counting method
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
光学手法による定量的生体計測技術
Quantitative analytical methods for biological systems in vivo by means of the optical technology
研究の背景 Background
生体は協同的に機能する階層システムであり、その理解のためには非破壊的な定量計測技術が必須である。また、このような計測がヒトレベルに応用可能であると、医学的に極めて有用な手法と成り得る。このような非破壊的測定の中で、光学的手法は生体分子特異的に計測することが可能な方法であり、広く応用されてきている。しかし、組織あるいは個体レベルにおいては、強い散乱と吸収による影響がその計測を極めて難しくしており、それらの影響を軽減させる計測手段とそれらを考慮した解析手法の開発が求められている。
The biological system is a cooperative hierarchical system and thus non-invasive analytical methods are required to understand the system. Further, this kind of methods for human is very useful in medical applications. The optical methods among non-invasive methods have a great advantage to measure biological molecules and are significantly investigated. However, the strong scattering and absorption of tissue prevent simple analyses in case of an organ or a body level size sample. The methods to overcome these problems are really needed for quantitative analysis.
研究の目標 Outcome
生体組織の散乱および吸収が少ない近赤外波長領域を用い、そこでの光伝播特性を解析し定量的な生体関連物質あるいは生体モニター分子プローブの定量化手法を確立する。特に、時間分解手法を用いて生体組織透過光の時間応答特性を解析し、そこから吸収あるいは蛍光を定量する実験的手法と理論的解析手法を確立する。さらに、ゆらぎ計測を用いて、動的な情報を得る方法論とその応用について確立し、医用への応用の基盤技術を創生する。
We investigate methodologies on time-domain near-infrared spectroscopy to quantify the biological molecules and biological monitoring probes in biological tissues. In particular, we are focusing a time-domain method to extract the spatial information, which is lost by the scattering, and aiming to establish the experimental and theoretical methods to quantify the probes. Further, we also wish to combine intensity fluctuation analyses, to quantify the dynamical information in tissue. Finally, we extend our methods to the medical applications
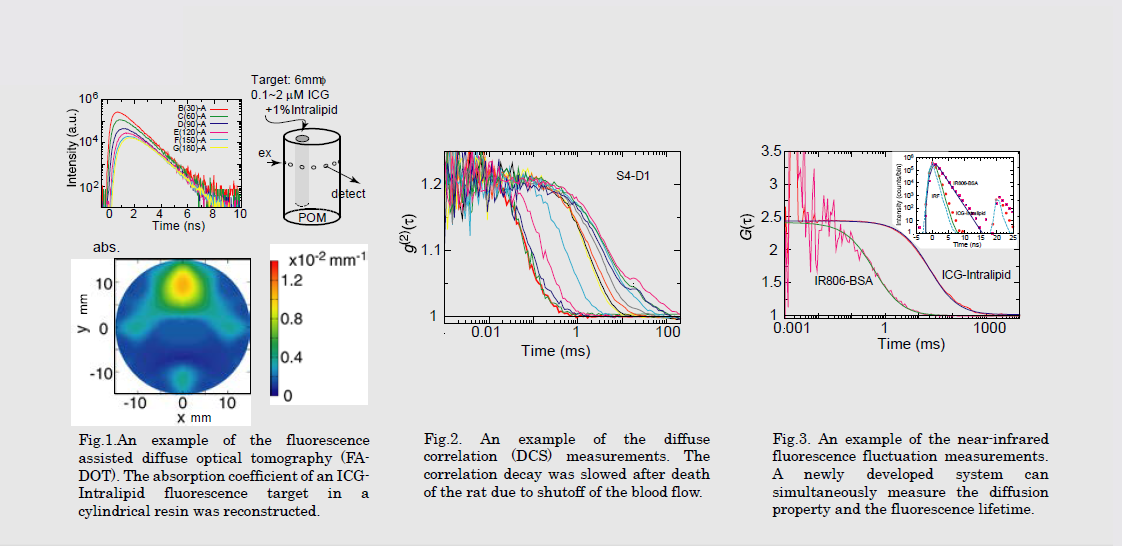
研究図Research Figure
文献 / Publications
RSC Advance, 4, 41164 (2014). SPIE Proc., 8578, 85782B (2013). Photochem.Photobiol.Sci. 10, 461 (2011). SPIE Proc., 7896, 78962Q (2011). Exp.Mol.Pathol. 82, 175 (2007).
研究者HP
- gnishi
 imd.es.hokudai.ac.jp
imd.es.hokudai.ac.jp - http://bppc03.es.hokudai.ac.jp/~gnishi/