
IMRAM
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
東北大学
多元物質科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/05/04
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name助永壮平 Sohei SUKENAGA
准教授 Associate Professor -
所属
Affiliation東北大学 多元物質科学研究所
プロセスシステム工学研究部門 材料分離プロセス研究分野
Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University
Division of Process and System Engineering, Materials Separation Processing -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords高温酸化物融体、過冷却液体およびガラスの物性計測および構造解析
金属製精錬スラグ、フラックス、放射性廃棄物のガラス固化体
Physical property measurement and structural characterization of oxide melts, super-cooled liquids, and glasses
Metallurgical slags, fluxes, and vitrified nuclear waste
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
構造情報に基づいた高温酸化物溶媒およびガラス材料の高機能化
Improving function of oxide solvent and glasses based on structure
研究の背景 Background of the Research
酸化物融体は、金属製精錬や有価金属のリサイクル、放射性廃棄物処理用溶媒として不可欠な液体材料である。また、酸化物融体を冷却して得られるガラス材料も様々な用途で使用されている。一方で、これらのランダム系材料においては物性(例:粘度、溶解度、熱伝導度、表面張力など)の組成や温度依存性発現メカニズムが十分に理解されていない。そのため、溶媒やガラス材料として求められる機能性を最大化するための指針が得られていない。
Molten oxides are indispensable solvent materials used in high-temperature industries, e.g., metallurgical processes and nuclear waste vitrification. Also, oxide glasses, which can be obtained by cooling the melts, have been widely used as fundamental and functional materials. However, the mechanism of the variations in their properties with the change in composition and temperature remains unclear. It has still been challenging to maximize the function of these disordered materials without understanding the mechanism.
研究の目標 Research Objective
融体やガラスの「高精度物性計測(粘度、熱伝導度、表面張力)」と核磁気共鳴やラマン分光法による「構造解析」を行い、物性と相関する構造情報を明らかにすること目指して研究を進めている。構造制御により溶媒やガラス材料の機能性を最大化させることが最終的な目標である。
To correlate the properties with structure, we have been conducting the “precise measurements of physical properties (e.g., viscosity, thermal conductivity, surface tension) for the molten oxides and glasses” and “structural characterization of these materials” using nuclear magnetic resonance and Raman Spectroscopies. Our goal is to maximize the function of the disordered oxide materials by controlling the structure.
研究図Figures
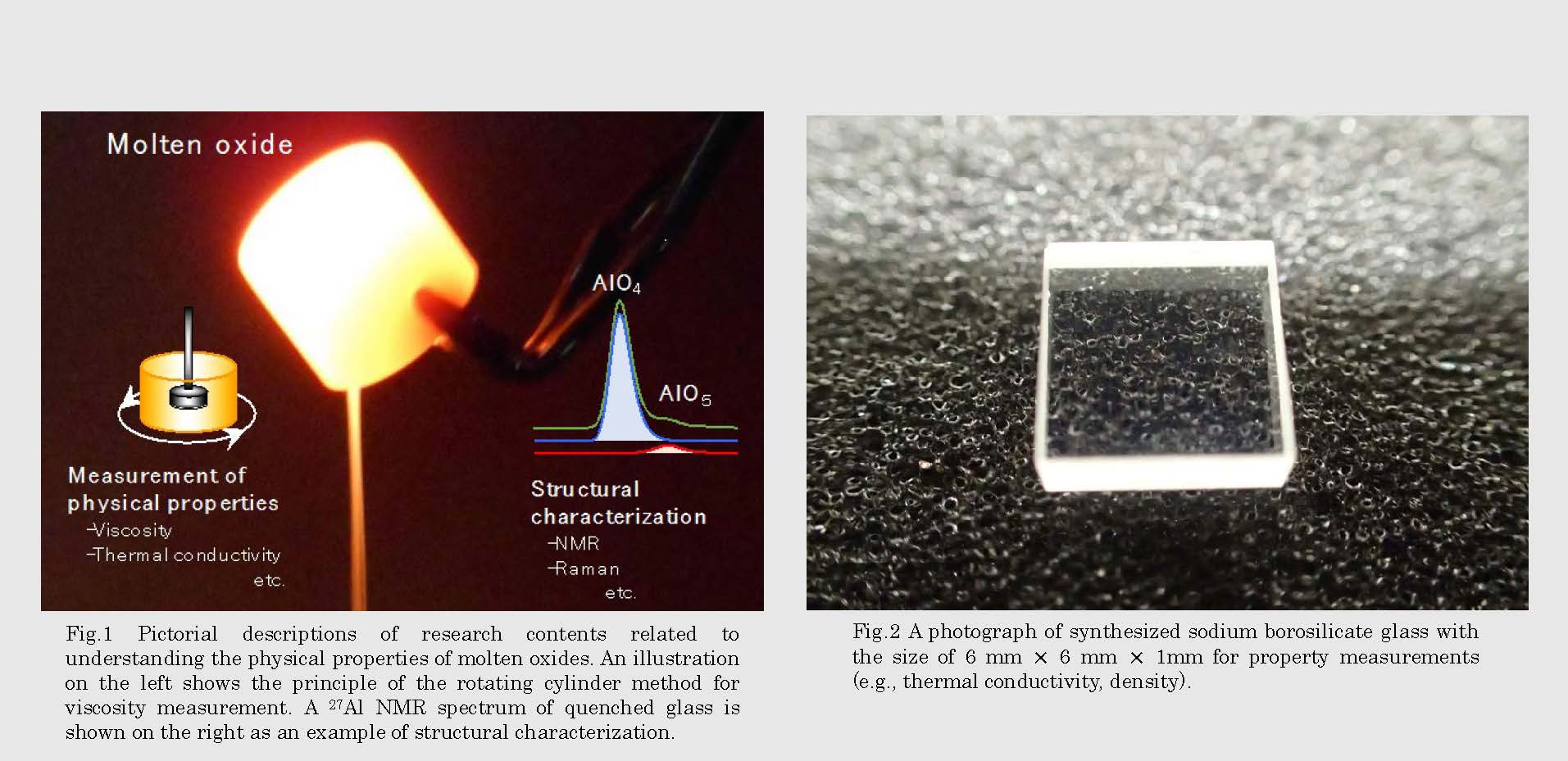
Fig.2 A photograph of synthesized sodium borosilicate glass with the size of 6 mm 6 mm 1mm for property measurements (e.g., thermal conductivity, density).
論文発表 / Publications
物性測定: Front Mater, 8(2021), 753746 (10.3389/fmats.2021.753746)., ISIJ Int, 60(2020), 2794 (10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2020-326).
構造解析: J Non-Cryst Solids, 587 (2022), 121600 (10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2022.121600)., J Phys Chem Lett,8(2017), 2274 (10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00465).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- sohei.sukenaga.d3
 tohoku.ac.jp
tohoku.ac.jp - http://www2.tagen.tohoku.ac.jp/lab/shibata/