
SANKEN
The University of Osaka
大阪大学
産業科学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2021/06/15
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name山田裕貴 Yuki YAMADA
教授 Professor -
所属
Affiliation大阪大学 産業科学研究所
エネルギー・環境材料研究分野
SANKEN, The University of Osaka
Department of Energy and Environmental Materials -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords二次電池
電解液
電気化学
Rechargeable batteries
Electrolyte
Electrochemistry
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
次世代蓄電デバイスの開発
Development of next-generation energy-storage devices
研究の背景 Background of the Research
現在、最も優れた二次電池とされているのがリチウムイオン電池であり、スマートフォンやノートパソコン、電気自動車用のバッテリーとして使われています。一方、リチウムイオン電池の唯一の欠点とされているのが安全性です。燃えやすい有機溶媒を含む電解液が採用されているため、発火・爆発事故が多く報告されています。したがって、安全かつ高性能の二次電池の開発が求められています。
Lithium-ion batteries, which are the best rechargeable batteries at present, are widely used in smartphones, notebook computers, and electric vehicles. However, they have serious safety hazards of fires and explosions because they employ highly flammable organic electrolytes. Therefore, the development of safe and high-performance rechargeable batteries is urgently required.
研究の目標 Research Objective
本研究では、難燃性かつ高性能の新規電解液材料の開発を行っています。具体的には、電解液に含まれるイオンと溶媒分子の配位状態を制御するという独自の設計戦略に基づき、従来の電解液にはない新機能・新物性の発現を目指します。特に、難燃性有機溶媒や水に着目し、配位状態制御によって高い耐電圧性を持つ難燃性電解液を開発していきます。
Our group is engaged in the development of non-flammable and high-performance electrolyte materials. Through our original strategy of controlling the coordination states of ions and solvent molecules, we are developing new functions and properties that are not found in conventional electrolytes. Focusing on flame-retardant organic solvents or ultimately water, we are designing nonflammable electrolytes with wide voltage windows.
研究図Figures
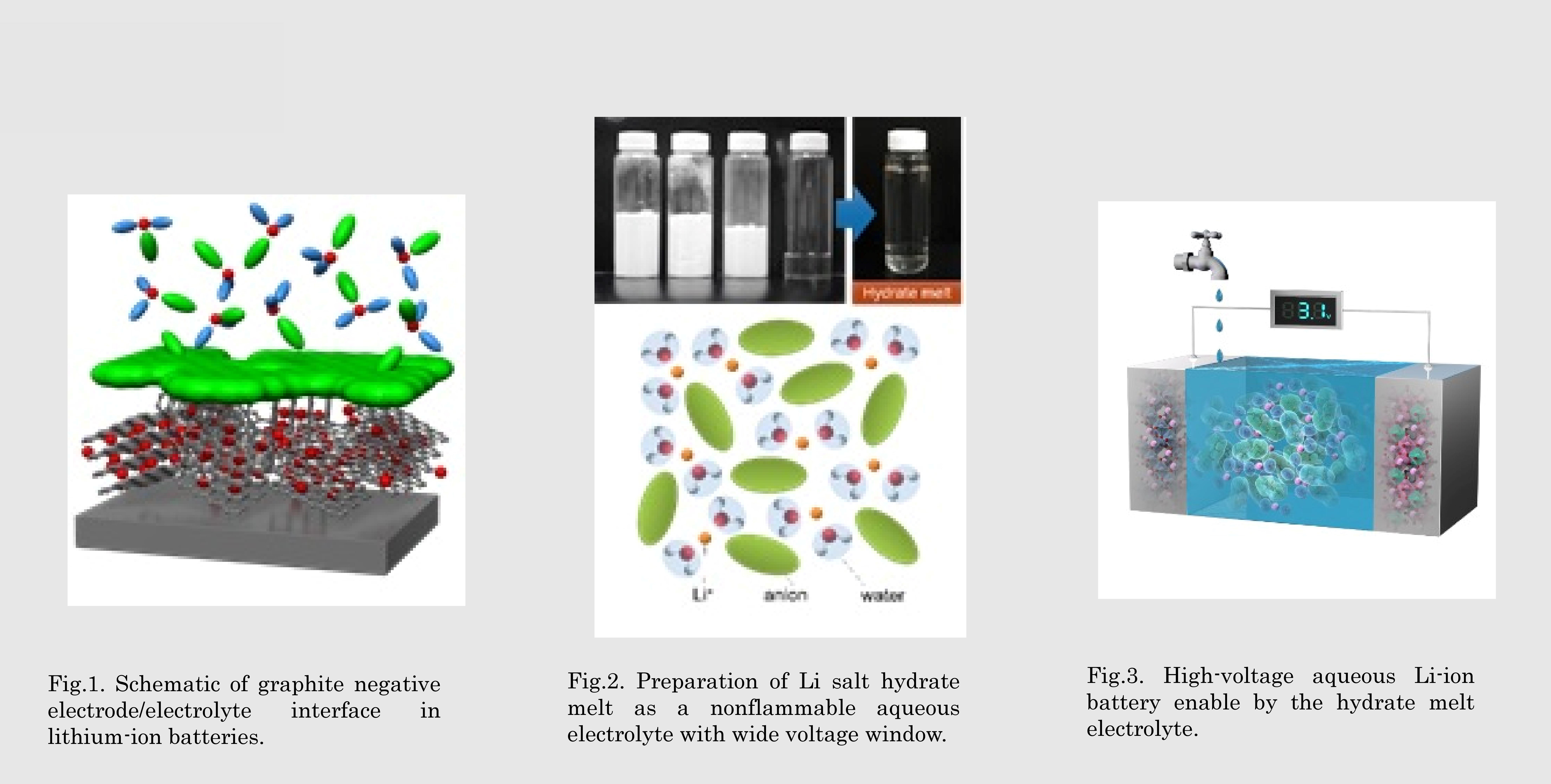
Fig.2. Preparation of Li salt hydrate melt as a nonflammable aqueous electrolyte with wide voltage window.
Fig.3. High-voltage aqueous Li-ion battery enable by the hydrate melt electrolyte.
論文発表 / Publications
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 5039 (2014). Nat. Commun. 7, 12032 (2016). Nat. Energy 1, 16129 (2016). Nat. Energy 3, 22 (2018). Nat. Energy 4, 269 (2019). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 8024 (2019). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.58, 14202 (2019). Nat. Energy 5, 291 (2020). Joule 5, 998 (2021).
研究者連絡先 / HP
- yamada
 sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp
sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp - https://www.sanken.osaka-u.ac.jp/organization/sec/sec_04/