IMCE
Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University
九州大学
先導物質化学研究所

LAST UPDATE 2017/02/25
-
研究者氏名
Researcher Name伊勢裕彦 Hirohiko ISE
准教授 Associate Professor -
所属
Professional Affiliation九州大学先導物質化学研究所
分子集積部門 生物物理化学分野
Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering, Kyushu University
Laboratory of Biomedical and Biophysical Chemistry, Department of Applied Molecular Chemistry -
研究キーワード
Research Keywords糖鎖
細胞骨格
バイオマテリアル
糖鎖高分子
Glycochain
Cytoskeleton
Biomaterials
Glycoside polymer
- 研究テーマ
Research Subject -
N-アセチルグルコサミン糖鎖高分子の細胞認識を用いた医療材料の開発
Development of medical materials using N-acetylglucosamine-bearing polymers
研究の背景 Background
生体に存在する糖鎖は、細胞認識や免疫応答など様々な生理機能を担っている。この生体の糖鎖を模倣した糖鎖高分子は、生体の機能制御において大変有益である。近年、N-アセチルグルコサミン(GlcNAc)を有する糖鎖高分子が細胞表面に出現した細胞骨格分子であるビメンチンやデスミンに対して高い相互作用を有することを明らかにしてきた。このことから、GlcNAc糖鎖高分子を用いることで、ビメンチンやデスミンを標的とした様々な医療材料への応用が期待できる。
Glycoside chains play many important roles such as cell-recognition and immune reactions. Bio-mimicking glycoside-bearing polymers are useful to regulate various cellular functions. Recently, we have reported that N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) bearing polymers interacted with cytoskeletal proteins, vimentin and desmin on cell surface. These findings are expected to able to develop various medical materials by using GlcNAc-bearing polymers.
研究の目標 Outcome
細胞骨格分子として知られるビメンチンは、様々な慢性炎症性疾患(ガンや自己免疫性疾患、線維症など)の疾患部位において高発現することが知られている。従って、GlcNAc糖鎖高分子を用いてビメンチンを標的化することで、ガンなどの様々な慢性炎症性疾患に対する分子標的薬や生体イメージングの実現が期待できる。本研究では、ビメンチンに対して高い相互作用を有するGlcNAc糖鎖高分子を設計して、ビメンチンを標的とした様々な医療材料の開発を目指している。
Cytoskeletal protein, vimentin is known to highly express at the area of various chronic inflammatory diseases such as cancers and fibrosis. Therefore, targeting of vimentin by using GlcNAc-bearing polymers is useful to develop molecular targeting reagents and bioimaging system for various chronic inflammatory diseases. In this study, we aim to design new GlcNAc-bearing polymers that are able to highly recognize vimentin and develop various medical materials for treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases by using GlcNAcbearing polymers..
研究図Research Figure
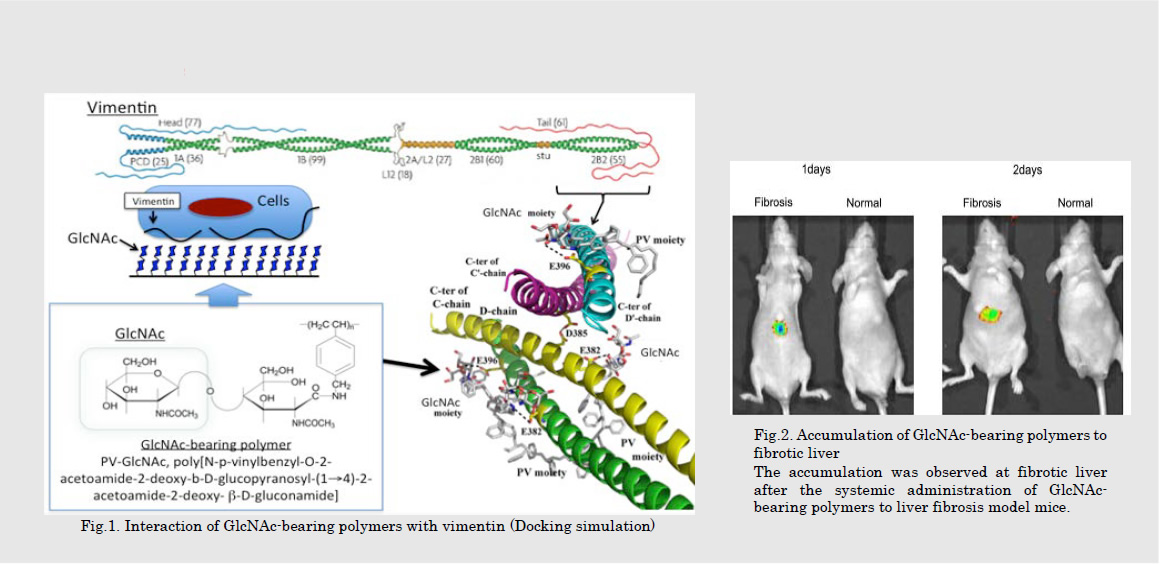
文献 / Publications
Biomaterials. 34, 6504-6514 (2013). Glycobiology. 22, 1741-1759 (2012). Biomaterials. 33, 2154-2164, (2012). Glycobiology. 20, 843-864 (2010)
研究者HP
- ise
 ms.ifoc.kyushu-u.ac.jp
ms.ifoc.kyushu-u.ac.jp - http://www.cm.kyushu-u.ac.jp/mbbmc_imce_new/